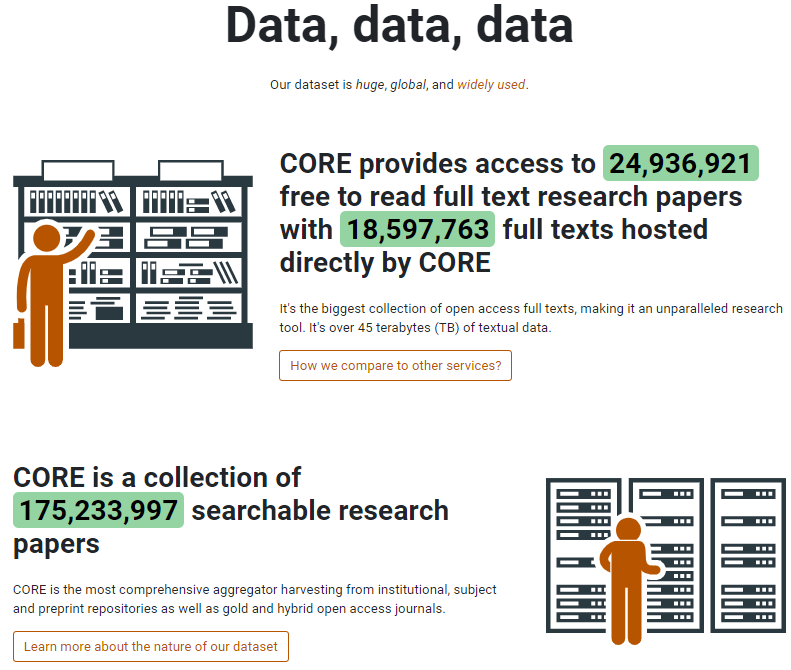
Since the start (10 years ago!) CORE’s mission has been to aggregate and facilitate access to Open Access scientific research at an unprecedented scale to both humans and machines. To achieve this aim, we are always refining and improving our methods for access and use of the CORE data.

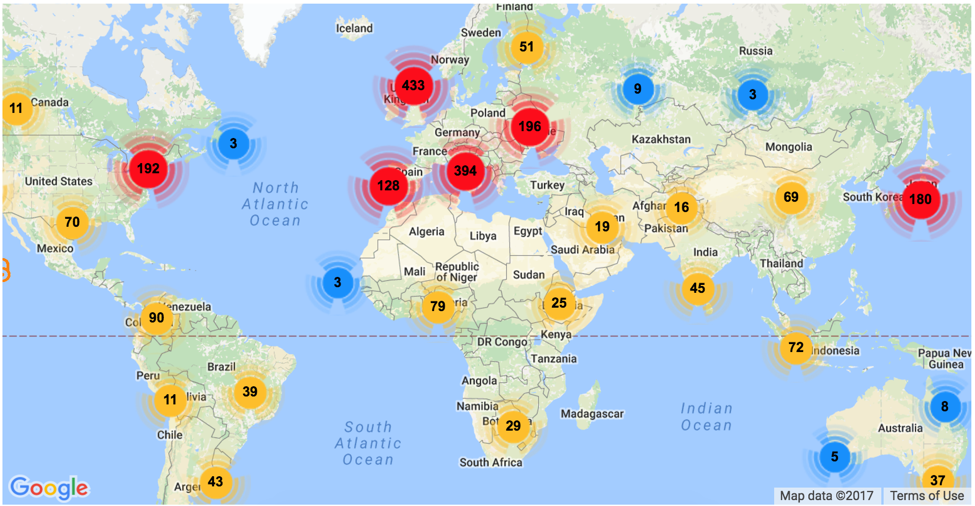
A key consideration in making improvements is that CORE users hail from many different backgrounds and are applying the CORE tools in a variety of use-cases. At last count, we had over 40 broad industry types (including academic research, education, publishing, software, and technology companies) applying the CORE tools to their work across the world. Applications of CORE tools and data are growing and constantly changing.